Best Energy-Efficient Windows Available Worldwide: A Comprehensive Guide
Delving into the realm of energy-efficient windows on a global scale, this guide aims to shed light on the best options available worldwide. With a focus on sustainability and innovation, readers are invited to explore the landscape of window technology designed to enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
The following paragraphs will delve into the various types of energy-efficient windows, the materials used in their construction, the cutting-edge technologies incorporated, and the significance of energy efficiency ratings and standards.
Types of Energy-Efficient Windows
Energy-efficient windows are designed to minimize heat loss and reduce energy consumption. There are several types of energy-efficient windows available worldwide, each offering unique features and benefits.
Double-Pane Windows
Double-pane windows consist of two panes of glass separated by a space filled with insulating gas, such as argon or krypton. This design helps reduce heat transfer and improve insulation, making them more energy-efficient than single-pane windows.
Triple-Pane Windows
Triple-pane windows have an additional pane of glass, providing even better insulation and energy efficiency compared to double-pane windows. The extra layer helps reduce noise transmission and enhances thermal performance, making them ideal for extreme climates.
Low-E Coated Windows
Low-emissivity (Low-E) coated windows have a thin, transparent coating that reflects heat while allowing light to pass through. This helps regulate indoor temperatures by reducing heat loss in winter and minimizing heat gain in summer, resulting in energy savings year-round.
Gas-Filled Windows
Gas-filled windows are filled with insulating gases, such as argon or krypton, to enhance their thermal performance. These gases are denser than air, reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency. Gas-filled windows are often combined with Low-E coatings for maximum benefits.
Smart Windows
Smart windows use technology to adjust tint levels based on sunlight exposure and temperature. They can automatically control the amount of light and heat entering a building, optimizing energy efficiency. Smart windows offer convenience and energy savings by reducing the need for heating, cooling, and artificial lighting.
Comparing Energy Savings
When comparing the energy-saving capabilities of different window types, factors such as U-factor, Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC), and Visible Transmittance (VT) should be considered. Triple-pane windows typically offer the highest energy efficiency, followed by double-pane windows with Low-E coatings and gas fills.
Smart windows provide additional benefits through automated energy management.
Materials Used in Energy-Efficient Windows
When it comes to energy-efficient windows, the choice of materials plays a crucial role in determining their performance. The materials used not only affect the sustainability and durability of the windows but also impact their energy efficiency.
Common Materials for Energy-Efficient Windows
- 1. Vinyl: Vinyl windows are popular for their energy efficiency, low maintenance, and affordability. They provide good insulation and are resistant to moisture, making them a durable choice.
- 2. Fiberglass: Fiberglass windows are known for their strength, durability, and energy efficiency. They offer excellent insulation properties and are resistant to warping, expanding, and contracting, ensuring long-term performance.
- 3. Wood: Wood windows have a classic look and provide natural insulation. When properly maintained, wood windows can be highly energy-efficient. However, they require more upkeep compared to other materials.
- 4. Aluminum: Aluminum windows are lightweight, strong, and low-maintenance. While aluminum is not as thermally efficient as other materials, newer designs with thermal breaks can improve energy efficiency.
Sustainability and Durability of Materials
- 1. Vinyl and fiberglass windows are considered more sustainable choices as they can be recycled at the end of their lifespan, reducing environmental impact.
- 2. Wood windows, while natural and renewable, require careful maintenance to ensure longevity and sustainability.
- 3. Aluminum windows, though durable, have a higher carbon footprint due to the energy-intensive manufacturing process. However, advancements in technology are making aluminum windows more energy-efficient and sustainable.
Impact on Energy Efficiency
- 1. The thermal properties of the materials directly impact the energy efficiency of windows. Materials with high insulation values help in reducing heat transfer, keeping the indoor temperature stable and reducing the need for heating or cooling.
- 2. Proper installation and sealing also play a vital role in maximizing the energy efficiency of windows, regardless of the material used.
- 3. Choosing the right material based on the climate and location of the building can significantly improve energy savings and overall comfort.
Technologies Incorporated in Energy-Efficient Windows
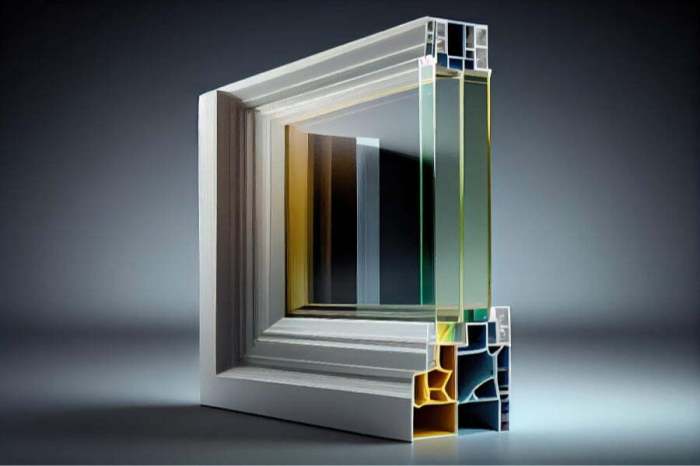

Energy-efficient windows incorporate a variety of innovative technologies designed to improve insulation, reduce heat transfer, and enhance overall energy efficiency in buildings. These technologies play a crucial role in lowering energy consumption, reducing utility costs, and minimizing environmental impact.
Low-E Coatings
Low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings are thin layers of metallic oxides applied to the glass surface of windows. These coatings help to reflect infrared heat while allowing visible light to pass through, resulting in improved insulation and reduced heat transfer. By minimizing heat gain in the summer and heat loss in the winter, Low-E coatings contribute significantly to the energy efficiency of windows.
Gas Fills
Energy-efficient windows often feature gas fills, such as argon or krypton, in the space between the glass panes. These gases are denser than air, providing better thermal insulation and reducing heat transfer through the window. Gas fills help enhance the overall energy efficiency of windows by improving their insulation properties.
Warm Edge Spacers
Warm edge spacers are components that separate the glass panes in double or triple-pane windows. These spacers are made from materials with lower thermal conductivity than traditional aluminum spacers, reducing heat loss around the window edges. By minimizing heat transfer at the edges, warm edge spacers contribute to the energy efficiency of windows.
Smart Technologies
Advancements in smart technologies have led to the development of energy-efficient windows with features like automated shading, dynamic glazing, and integrated sensors. These technologies allow windows to respond to changing environmental conditions, optimizing natural light, heat gain, and privacy. By adapting to external factors, smart technologies improve window performance and overall energy efficiency in buildings.
Energy Efficiency Ratings and Standards

In the realm of energy-efficient windows, understanding energy efficiency ratings and standards is crucial for both manufacturers and consumers. These ratings help assess the performance of windows in terms of energy conservation and insulation capabilities, guiding consumers in making informed choices and encouraging manufacturers to produce more sustainable products.
Global Rating Systems
- ENERGY STAR: One of the most widely recognized energy efficiency rating systems, ENERGY STAR certification indicates that a window meets or exceeds specific energy performance criteria set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
- European Union Energy Label: The EU energy label provides information on the energy efficiency of windows based on a scale from A++ to G, with A++ being the most efficient.
- National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC): The NFRC label in the United States rates windows based on factors like U-factor, solar heat gain coefficient, visible transmittance, and air leakage.
Significance of Meeting Standards
Meeting energy efficiency standards in window manufacturing is essential for reducing energy consumption, lowering utility costs, and minimizing environmental impact. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can contribute to energy conservation efforts and offer high-quality products that benefit both consumers and the planet.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the world of energy-efficient windows offers a multitude of options for environmentally conscious consumers seeking to optimize energy savings and enhance the comfort of their living spaces. By prioritizing sustainability and technological advancement, choosing the best energy-efficient windows available worldwide becomes not just a necessity, but a statement towards a greener future.
Helpful Answers
What are the benefits of energy-efficient windows?
Energy-efficient windows help reduce energy consumption, lower utility bills, improve indoor comfort, and decrease carbon footprint.
How do energy-efficient windows impact the environment?
Energy-efficient windows reduce the need for heating and cooling, thus lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production.
Are energy-efficient windows more expensive than regular windows?
Initially, energy-efficient windows may have a higher upfront cost, but the long-term savings on energy bills usually make them a cost-effective choice.